An increasing number of Pharma companies are investing in automation strategies to improve the activities and services offered. According to the study by The Association for Packaging and Processing Technologies, about 50% of pharma and medical device companies are implementing the integration of line automation and will continuously monitor the overall effectiveness of the equipment. They are introducing cobots (collaborative robots), that is industrial robots designed to work safely together with humans, without protective barriers or other physical elements of separation, equipped with safety and anti-collision systems, as well as cameras and sensors, which allow the sharing of spaces with the workers on the line, without risk of accidents, as provided for in remainder from ISO 10218 / TS 15066.
In order to work side by side with people, cobots must meet high safety requirements, must be able to perceive external forces and be able to stop promptly in the event of impact or contact. A fundamental requirement for collaborative applications is in fact that of not causing injury to people in the collaborative work space, should an accidental impact occur; an impact can in fact cause damage to the operator.
They are specialized machines, “trained” to carry out certain tasks with greater or lesser levels of autonomy, which are increasingly used on production lines. Cobots limit some of the environmental and spatial disadvantages of using traditional robots, as they limit the space occupation of the packaging lines and are more suitable for small-medium scale packaging activities. These systems are becoming more and more widespread in the current panorama of the production of micro-batch drugs.
GUARANTEED PROTECTION
The AW-Tube modular cobot is equipped with various safety functions.
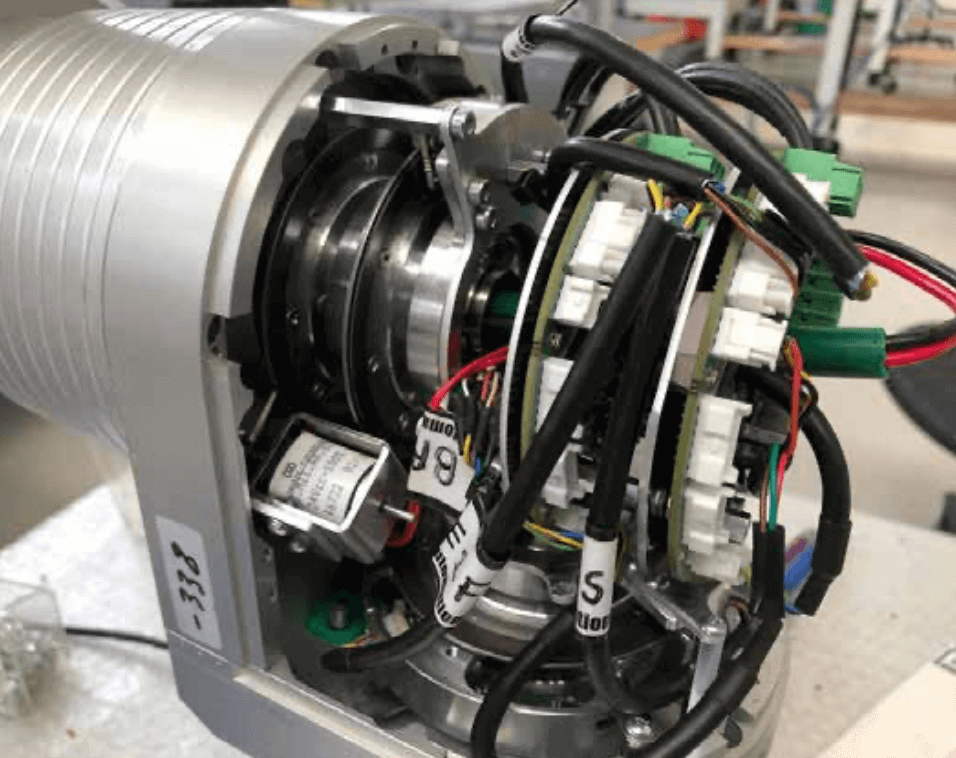
Entry level: AW J-Actuator couplings feature a motor and sensor control board, with dual processor control. This configuration guarantees continuous functionality in the event of a processor malfunction, which in the second instance performs the safety actions of the robot joint. Each processor is independent and controls the sensors in the system. In the basic configuration, the processors control the resulting torque in the joint by measuring the current. For maximum accuracy, it uses a 12-bit digital sampling system (ADC), and again each processor incorporates an ADC. If the current exceeds the preset values (according to the recommendations of EN ISO 10218-1), the processor blocks the robotic joint.
Medium level: the J actuators have a three-dimensional accelerometer in the robotic joint which allows, in case of accidental contact with things or people, to detect an electrical signal with very high sensitivity. Obviously, the accelerometer has 3 measurement channels to ensure that all or part of them detect contact. The device is very sensitive and the detection threshold is programmable up to 10 Nm. Obviously, in multi-articulated robotic compositions, multi-channel diagnostics can be available to manage each sensory cell on the network. This method is patented by AutomationWare (AwareVu) and allows the observation of the kinematic variations of the moving system.
High level: in the J actuators there are 2 20-bit absolute magnetic encoders. These devices control the rotation speed of 2 axes installed in the joint (fast and slow axis). This procedure complies with the EN standards…. which provide for the redundancy of the joint rotation reading device. If an axis freezes for mechanical reasons, the system stops the robot. However, the use of very precise encoders also allows the verification of the torsional stiffness of the system, highlighting any effects of impedance, due to unexpectedly very high loads. Also in this case the processors that control the two encoders, thanks to an algorithm patented by AutomationWare, can block the robot in case of excessive torsional variations.
Extreme level: J actuators are controllable in the ROS environment. The use of cameras in the robotic joints allows you to determine safe operating areas,
inside which no objects or people can enter. In the event of an invasion, the system will block the arm or robotic configuration.
In addition to safety, another important feature of AutomationWare’s AW-Tube cobot is its modularity, as the customer requires a product tailored to their application, with payload, number of axes and operating area specific to their needs.










